What is the NIST AI RMF?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Artificial Intelligence Risk Management Framework is a voluntary framework released in 2023 that helps organizations identify and manage the risks associated with development and deployment of Artificial Intelligence. It is similar in its intent and structure to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) which has become a global standard for managing cyber risks.
Who is it intended for?
The AI RMF is intended for organizations of any size ranging from startups to government agencies. As a federally proposed framework, it is particularly relevant to organizations working with the US government, although NIST frameworks have also been adopted by other countries. By focusing on outcomes and end states, rather than prescribing steps, the NIST framework is also applicable to organizations with different AI expertise and risk tolerances.
If the framework is ‘voluntary’, why should I care?
It is highly likely that regulators both in the US and abroad will use it as a baseline for mandatory risk management and vendor procurement requirements. This follows a similar path to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework which is also technically voluntary, but is now required by law for federal agencies, many state governments, the Securities Exchange Commission, and by soft law groups both in the US and internationally. The Biden Administration is considering requiring the NIST AI RMF for all federal use of AI, and this likely will have a trickle down effect to all organizations receiving federal funding. Similarly, the framework may be used by organizations for their own procurement purposes, and demonstrated compliance with the framework can increase customer trust in an AI product.
How does it compare to the EU AI Act?
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act) is a deliberately broad law being finalized in the EU to govern commercial AI products. The AI act identifies certain types of ‘high risk’ use cases of AI that come with the heaviest compliance requirements. One of those key provisions is Article 9, which requires ‘high risk’ AI system developers to adopt a ‘Risk Management Framework’. Additional guidance on this framework is expected some time after the passage of the AI Act (likely early 2024) however implementing the NIST AI RMF will help organizations prepare for compliance with this provision in advance. The AI Act has additional compliance requirements not covered by the NIST AI RMF such as regular government incident reporting, and internal audits.
How does it compare to ISO 23894-2023 ?
International Standards Organization (ISO) 23894 is a publication that adapts the generic risk management framework from ISO 38001-2018 to Artificial Intelligence. It outlines some of the types of risks unique to AI systems, and how an organization can adapt their existing risk management processes to account for this. This publication primarily focuses on the risk to the organization however and focuses heavily on the organizational policies and processes that need to be in place to manage this risk. There is a large amount of overlap between NIST AI RMF’s and the principles and controls recommended in ISO 23894.
How does it compare to ISO 42001-2022 ?
ISO 42001 is an upcoming standard for a management system for artificial intelligence. It is similar to ISO 23894 in that it heavily considers AI risk, however it also offers recommendations for best practices for additional organizational governance and AI quality management. ISO 42001 provides deeper guidance on overall organizational governance controls for AI,offering recommendations for best practices for additional organizational AI governance and quality management. It complements the NIST AI RMF which is less descriptive about exact controls organizations should have in place.
What do I need to do to comply with NIST?
The NIST AI RMF has 4 key components to it. It outlines what kinds of policies and roles should be in place to govern AI systems, how to map the business and legal context of each application of AI to relevant risks, how to measure the likelihood, severity and impact of these risks, and how to appropriately manage these risks. The AI RMF focuses on ensuring that the risks to people, organizations, and society from AI systems are identified and mitigated.
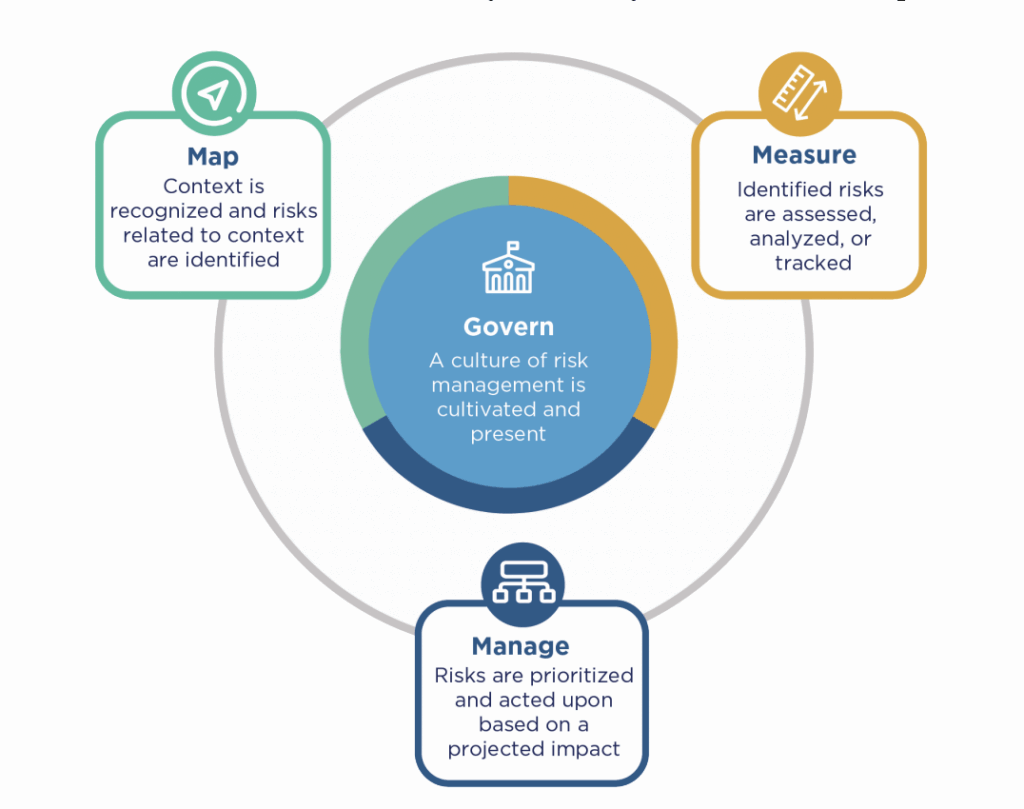
4 Components of the NIST AI RMF
How do I get started adopting the framework?
To learn more about the framework, NIST has published a ‘playbook’ which includes additional context and best practices for each of the framework’s components. Each component (GOVERN, MAP, MEASURE, MANAGE) prescribes specific practices that an organization should implement. There is flexibility in the exact controls depending on the organization’s overall risk tolerance and resources. After identifying the relevant policies, organizations should start building out an inventory of their applications of AI. This AI Application inventory is different from previous model inventories. In the age of general purpose foundational models, tracking models alone is insufficient as many of the risks are directly tied to the system’s goals, how the system is deployed, as well as what domain/industry it is deployed in.
How does Trustible help me with the NIST AI RMF?
The Trustible Responsible AI Governance platform uses the NIST AI RMF as a core part of its product roadmap. Trustible can help your organization identify and develop the AI policies required by the NIST AI RMF. Once those policies are drafted, the platform helps organizations implement those policies by assisting with documentation, automated workflows, and recommending relevant risks for each use case of AI. Finally, Trustible connects into your existing ML tools to help generate proof that appropriate risk mitigation practices are in place, with reports mapping each component of the NIST AI RMF to verify compliance.



